

Even with improved tools, more businesses are facing network security vulnerabilities than ever. Attackers continue to find gaps because systems change rapidly, and teams often fall behind in security.
According to IBM’s 2023 Cost of a Data Breach Report, 83% of organizations experienced more than one data compromise in 2022. Besides hackers being more brilliant, it’s about defenders not having the proper visibility.
Henry D. Overton, President and Co-Founder of Turn Key Solutions, says, “No solution works unless your people and processes support it. Tools are only as good as the gaps they cover.”
This blog breaks down how network vulnerabilities keep growing, what attackers are targeting, and what you can do to protect your business.
Eliminate the Gaps That Invite AttacksTurn Key Solutions helps you patch weak spots before they’re exploited. |
What Makes Networks So Easy to Exploit?
Network vulnerabilities are weaknesses in your digital environment that attackers can use to gain access or disrupt operations. These are not always active attacks. Many are dormant issues, such as unpatched software or poor configurations, waiting for hackers to discover.
The difference between cybersecurity vulnerabilities and threats is that vulnerabilities are gaps. Threats are the actual attempts to exploit those gaps. Attackers combine both. That’s why you can’t wait until there’s a problem.
Networks are easy to exploit because:
- Weak configurations: Improperly set up routers or firewalls allow unauthorized traffic, letting attackers bypass defenses.
- Unpatched systems: About 60% of cyber compromises result from unpatched vulnerabilities. Delayed software updates create backdoors, exposing systems to public exploits.
- Poor user behavior: Clicking suspicious links or reusing passwords makes it easy for attackers to gain access.
- Limited visibility: Without insight into vulnerabilities across devices, apps, or endpoints, weaknesses remain undetected and unfixed.
Each of these issues provides attackers with an opportunity. Together, they increase your risk without triggering alerts.
Common Network Vulnerabilities That Leave You Open to Attack
Every day tools and devices often contain common network vulnerabilities that many businesses ignore. These weaknesses don’t always look critical at first, but are among the most commonly used by attackers.
- Outdated operating systems: Without security patches, unsupported systems remain vulnerable to new threats and often lack monitoring tools.
- Misconfigured firewalls and switches: Improper rule sets and outdated firmware create blind spots, allowing unauthorized traffic into the network.
- Weak authentication setups: Simple or shared passwords make access easy for attackers, while multi-factor authentication is often overlooked internally.
- Improper device management: IoT devices, such as printers, smart TVs, and cameras, often remain unmanaged, thereby increasing security risks.
- Poor physical access control: Unrestricted access to servers or network ports makes digital protections useless if attackers can plug in devices or enter data rooms.
You can’t fix what you don’t track. These vulnerabilities often go unnoticed until hackers exploit them.
Types of Vulnerabilities in Network Security That Attackers Target First
When attackers scan a network, they look for the most exposed and least protected gaps. These types of vulnerabilities in network security provide a quick entry point and allow attackers to remain hidden for longer periods.
Software and System Vulnerabilities
Attackers often go after operating systems, applications, and firmware that you have refused to update.
These include:
- Zero-day exploits: Attacks on undisclosed vulnerabilities, making them highly targeted and dangerous.
- Unpatched OS/apps: Outdated Windows servers, unsupported databases, or abandoned plugins can grant remote access without credentials.
Many businesses delay updates to avoid disruptions. That creates bigger risks.
Human-Facing Cyber Vulnerabilities
People are the easiest entry point for attackers. While external actors are responsible for 65% of breaches, 35% result from employee errors rather than deliberate wrongdoing.
Common human-facing vulnerabilities include:
- Phishing, smishing, and social engineering: Deceptive tactics designed to trick users into revealing passwords or granting access. They are simple yet highly effective.
- Weak password practices: Reusing passwords or storing them in plain text makes long-term access easy for attackers.
These gaps can bypass technical protections completely because they depend on human error.
Infrastructure Weak Points
The way your network is designed also affects your risk exposure. Some common weaknesses include:
- Poor segmentation: Weak separation between departments, systems, or cloud and internal services allows attackers to move unrestricted once inside.
- Flat networks: Without barriers, attackers can move laterally across systems, making infiltration even more dangerous.
Good tools won’t fix a bad network layout. Segmentation is essential.
| More articles you might like: |
The Most Dangerous Types of Network Security Threats Right Now
Types of network security threats have evolved. Many combine several methods and move quickly across systems.
Below are the most damaging categories:
- Malware: Trojans, ransomware, and spyware steal data or lock systems, often entering through phishing emails or infected downloads.
- Botnets and DDoS attacks: Malicious actors hijack devices, including printers and smart thermostats, to overwhelm networks.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks: 35% of exploitations involved Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks. These attacks intercept and alter communications, commonly occurring on public Wi-Fi networks or those with poor security.
- SQL injection: Poorly coded websites and apps provide entry points to databases, making this one of the top ten attack methods.
- Logic bombs: Hidden malicious code within applications that activates under specific conditions.
- Advanced persistent threats (APTs): Stealthy, prolonged attacks where intruders stay undetected for weeks or months, gathering intelligence and planning disruptions.
Many of these threats target the same cyber vulnerabilities mentioned earlier. Once inside, attackers often stay quiet to avoid detection.
Why Cyber Threats and Vulnerabilities Are Getting Harder to Detect
Cyber threats and vulnerabilities are now more automated, personal, and adaptive. Attackers use tools that mimic user behavior or steal credentials instead of brute-forcing systems.
Here’s what makes them harder to detect:
- AI-driven phishing: Highly customized and convincing messages are designed to trick recipients, increasing the likelihood of engagement.
- Obfuscation tactics: Encryption and fileless malware help threats bypass security filters undetected.
- Legitimate credentials: Attacks appear as regular traffic when attackers use valid logins, making detection difficult.
Attackers rely on your blind spots. Once inside, they move slowly and quietly. Without real-time detection, these attacks often go unnoticed.
How to Reduce Network Security Vulnerabilities Without Overcomplicating IT
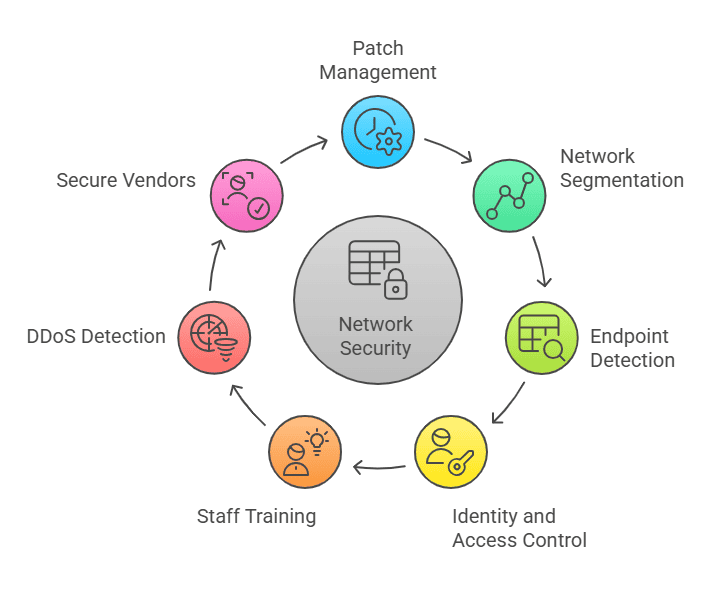 You don’t need more tools to improve security. You need better processes. Here are simple ways to reduce network security vulnerabilities without adding more complexity:
You don’t need more tools to improve security. You need better processes. Here are simple ways to reduce network security vulnerabilities without adding more complexity:
- Patch management policies: Enforce timely updates across all systems, including legacy tools, with automation where possible.
- Network segmentation: Prevents the spread of threats by dividing networks based on department, system type, or risk level.
- Endpoint detection tools: Monitor workstations, laptops, and mobile devices for signs of suspicious activity.
- Identity and access control: Ensure users access only what they need, applying the principle of least privilege and tracking account activity.
- Staff training and phishing simulation: Keep teams alert—users who recognize threats are the best defense.
- DDoS detection and alerting tools: Monitor traffic patterns to detect and prevent major disruptions early.
- Secure vendors and cloud solutions: Choose providers with verified audits, ongoing penetration tests, and clear security policies.
Each of these steps adds visibility, control, and response power without introducing additional layers of complexity.
Spotting Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities Before They’re Exploited
Fixing cybersecurity vulnerabilities after a problem happens is too late. You need to spot gaps before attackers do.
Here’s how:
- Vulnerability scanning: Regularly check systems for known risks, especially after significant changes.
- Penetration testing: Simulate real attacks to identify weaknesses and potential entry points.
- Baseline monitoring: Establish standard activity patterns to detect anomalies quickly.
- Real-time analytics and alerts: Enable rapid response to threats before they escalate.
- Remote users and unmanaged devices: Include them in your visibility plan, as many attacks originate from remote logins or personal devices.
Key Differences Between Vulnerabilities and Threats
Many organizations confuse vulnerabilities with threats. The table below outlines the differences and why each requires different actions. Knowing what you’re dealing with helps you respond correctly.
| Category | Vulnerability | Threat |
| Definition | A weakness or gap in security posture | A potential danger that exploits a vulnerability |
| Example | Unpatched software | Malware that uses unpatched software to enter |
| Control | Can be fixed through patching, reconfiguration, and training | Must be detected, blocked, and neutralized |
| Prevention Focus | System hardening, user education | Detection tools, response strategies |
Attackers need both. Your goal is to remove the first so the second can’t succeed.
Secure Every Gap with Turn Key Solution’s Cybersecurity Protection
Many businesses still rely on old methods to protect against modern threats. You don’t need more complexity. You need complete visibility and better process controls. XL.net helps you eliminate network vulnerabilities before they escalate into more significant issues.
As a trusted partner with over 25 years in business, Turn Key Solutions secures over 150 clients and more than 1500 endpoints.
| Trusted Cybersecurity Services Near You
|
We help small and midsize businesses spot gaps, secure systems, and train teams, without wasting time or budget. Contact us to schedule a consultation and learn how we protect your business from end to end.




